ņä£ ļĪĀ
ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØĆ ņé╝Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö Ēü¼ĻĖ░ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņ×æļÉśņ¢┤ ņåīĒÖöĻ┤Ć ļé┤ļČĆļź╝ ņ┤¼ņśüĒĢśļŖö ņØśļŻī ņןļ╣äņØ┤ļŗż. 2000ļģäļīĆ ņ┤łļ░śņŚÉ ņåīĻ░£ļÉśņ¢┤ ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖ ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Įņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ┤Ćņ░░ņØ┤ ņ¢┤ļĀżņÜ┤ ņåīņן ņ¦łĒÖśņØś ņ¦äļŗ©ņŚÉ ņżæņÜöĒĢ£ ņŚŁĒĢĀņØä ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņśüņāü ņ┤¼ņśüņØä ņ£äĒĢ£ Ļ┤æĒĢÖļČĆ, ļ¼┤ņäĀ ņĀäņåĪņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņåĪņŗĀļČĆņÖĆ ņØ┤ļōżņØä ĻĄ¼ļÅÖĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ ņĀäņøÉļČĆ ļČĆĒÆłļōżņØä ņé╝Ēé¼ ņłś ņ׳ļŖö Ēü¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ņ¦æņĢĮĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņåīņן ļČĆņ£ä ņ┤¼ņśüņŚÉ ņČ®ļČäĒĢ£ ņ×æļÅÖ ņŗ£Ļ░äņØ┤ ļ│┤ņןļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ļŗżļźĖ ņåīĒÖöĻĖ░ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ¼╝ļ”¼ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśļŖö ņØ╝ņŚÉ ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņØ┤ ļ¦Äļŗż. ņןĻ┤Ć ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ņŚ░ļÅÖ ņÜ┤ļÅÖņŚÉ ņØśņĪ┤ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņłśļÅÖņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØ┤ļÅÖĒĢśļ®┤ņä£ 5ļ¦ī ņןņØ┤ ļäśļŖö ļööņ¦ĆĒäĖ ņé¼ņ¦äņØä 4ņŗ£Ļ░ä ņØ┤ņāüņŚÉ Ļ▒Ėņ│Éņä£ ņ┤¼ņśüĒĢśļŖöļŹ░, ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņØśļ»Ė ņ׳ļŖö ļ│æļ│Ć ņśüņāüņØś ļČäļ¤ēņØĆ ņĀäņ▓┤ņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ļ¦żņÜ░ ņĀüļŗż[1,2]. Ļ▓īļŗżĻ░Ć ņØ┤ļź╝ ĒīÉļÅģĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ņåīņÜöļÉśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äļÅä ĻĖĖņ¢┤ ĒīÉļÅģņ×É Ļ░äņØś Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ ĒÄĖņ░©Ļ░Ć Ēü¼ļŗż.
ļööņ¦ĆĒäĖ ņśüņāüņØĆ ļ░ØĻĖ░ņÖĆ ņāēņāüņØ┤ ļŗżļźĖ ņØ╝ņĀĢĒĢ£ ņłśņØś ĒÖöņåīļōżļĪ£ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ļÉ£ļŗż. ņłśĒĢÖņĀü ņŚ░ņé░ņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņØ┤ļź╝ ņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśļŖö ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ ņśüņāüņØś ĒÆłņ¦ł Ē¢źņāü ļ┐Éļ¦ī ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņśüņāü ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ Ļ░Øņ▓┤ ņØĖņŗØņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņłśņżĆņŚÉ ņØ┤ļź┤Ļ│Ā ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░, ņØ┤ļŖö ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀü ĒĢ£Ļ│äļź╝ ĻĘ╣ļ│ĄĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒīÉļÅģ ĒÜ©ņ£©ņä▒ņØä Ē¢źņāüņŗ£ĒéżļŖö ļŹ░ ļÅäņøĆņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļ│ĖĻ│ĀņŚÉņä£ļŖö ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ĻĖ░ļŖź Ļ░£ņäĀņØä ļ¬®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀ£ņĢłļÉ£ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä Ļ░äļץĒ׳ ņåīĻ░£ĒĢśĻ│Āņ×É ĒĢ£ļŗż.
ļ│Ė ļĪĀ
ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØĆ ņ┤¼ņśü ņł£Ļ░äņŚÉ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņøĆņ¦üņ×äņØä ļ®łņČöĻ▒░ļéś Ļ┤æņøÉņØś ļ░ØĻĖ░ļéś ņ┤łņĀÉ Ļ▒░ļ”¼ļź╝ Ļ░ÉņĢłĒĢśņŚ¼ ļīĆņāüņŚÉ ņĀæĻĘ╝ņØä ņĪ░ņĀłĒĢśļŖö ļō▒ņØś ņĪ░ņ×æņØ┤ ļČłĻ░ĆļŖźĒĢśļŗż. ļśÉĒĢ£ ņ┤¼ņāüļČĆņØś ņä▒ļŖźļÅä ņØ╝ļ░ś ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Įļ│┤ļŗż ļ¢©ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻĖ░ ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ĒØÉļ”░ ņśüņāü(blurred image)ņØ┤ļéś, ņŗĀĒśĖ ņ×ĪņØī(noise)ņØ┤ ĒżĒĢ©ļÉ£ ĒÆłņ¦łņØ┤ ļé«ņØĆ ņśüņāüņØ┤ ņ¢╗ņ¢┤ņ¦ĆĻĖ░ ņēĮļŗż. ņØ┤ļź╝ Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ Ļ░£ļ░£ļÉ£ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ĒĢäĒä░ļōżņØä ļ╣äĻĄÉĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝, adaptive median filter (AM filter)Ļ░Ć ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņŚÉņä£ ļ¼śņé¼ļÉ£ ņäĖļČĆ ņé¼ĒĢŁņØś Ēø╝ņåÉņŚåņØ┤ ņ×ĪņØīņØä Ļ░ÉņćäĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśņŚłļŗż[3]. ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņØä ņä£ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ ņāēņāü ņ▒äļäÉļĪ£ ļČäļ”¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ░üĻ░üņØä ĒÜīņāēņĪ░ ņśüņāüņ£╝ļĪ£ ļ│ĆĒÖśĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ×¼ļČäņäØĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņĪ░ĒĢ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņśüņāüņØś ņ×ĪņØīņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśļŖö ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØ┤ ņĀ£ņĢłļÉśĻĖ░ļÅä ĒĢśņśĆļŗż[4].
ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ĻĄ¼Ļ░äņŚÉņä£ ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢ£ Ļ┤æļ¤ēņØ┤ļéś Ļ│╝ļÅäĒĢ£ ņøĆņ¦üņ×äņŚÉ ņØśĒĢ┤ ĒØÉļĀżņ¦ä ņśüņāüļÅä ĒÜīņāēņĪ░ļĪ£ ļ│ĆĒÖśĒĢśņŚ¼ ņłśņ╣ś ĒĢ┤ņäØņØ┤ ņÜ®ņØ┤ĒĢśļÅäļĪØ ņĀäņ▓śļ”¼ĒĢśĻ│Ā ņØ┤ļź╝ ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ Ļ│äņé░ĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņĀüņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│┤ņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[5]. ņĀäņ▓┤ ņśüņāüņØś ļ¦źļØĮņØś Ļ░ÉņĢłĒĢśņŚ¼ ļÅÖņØ╝ ļīĆņāüņØ┤ ņ┤¼ņśüļÉ£ ļŗżļźĖ ņןļ®┤ņØ┤ļéś ņŻ╝ļ│Ć ņןļ®┤ļōżņØä ņ░ĖņĪ░ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņśüņāü ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ĒĢ®ņä▒ĒĢ£ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļÅä ĒĢ┤ņäØņŚÉ ļÅäņøĆņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[6,7].
ĻĘ╝ļלņŚÉ Ļ░üĻ┤æļ░øĻĖ░ ņŗ£ņ×æĒĢ£ ļöźļ¤¼ļŗØ ĻĖ░ņłĀ ņŚŁņŗ£ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņśüņāü ĒÆłņ¦ł Ļ░£ņäĀņŚÉ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŖöļŹ░, ļīĆļ¤ēņØś ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņØä ĒĢÖņŖĄĒĢ£ ļöźļ¤¼ļŗØ ņĢīĻ│Āļ”¼ņ”śņØĆ ņŚ┤ĒÖöļÉ£ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņØä Ļ│ĀĒĢ┤ņāüļÅäļĪ£ ļ│ĄņøÉĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ĒÜ©Ļ│╝Ļ░Ć ņ׳ņŚłļŗż[8]. ĒŖ╣Ē׳, ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ņØä Ļ│ĀļĀżĒĢśņŚ¼ ņäżĻ│äļÉ£ ņĢīĻ│Āļ”¼ņ”śņØ┤ ļŹö ņóŗņØĆ ņä▒ļŖźņØä ļ│┤ņØĖ ļ░ö ņ׳ņ¢┤ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ĻĖ░ļŖź Ļ░£ņäĀņŚÉ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ņØ┤ ĻĖ░ļīĆļÉ£ļŗż.
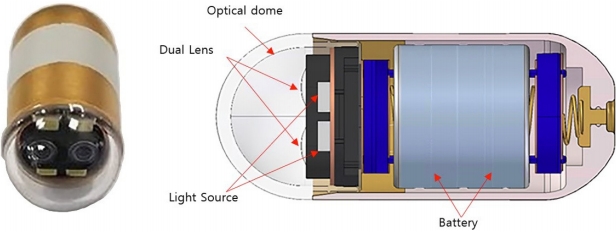
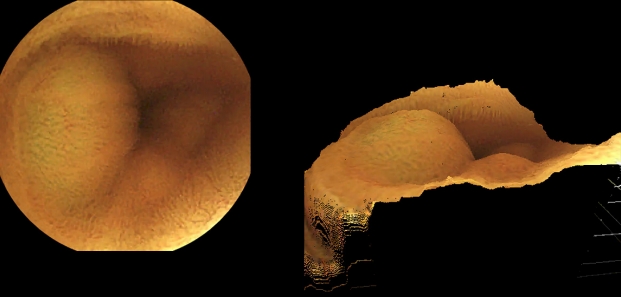
ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀüņØĖ Ļ░£ņäĀņØ┤ ļÆĘļ░øņ╣©ļÉśļ®┤ ļŹö ņŗżņÜ®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢśļŗż. ĻĖ░ņĪ┤ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØ┤ ĒĢ£ Ļ░£ņØś ĻĄ¼ļÅÖņČĢņŚÉņä£ ņśüņāüņØä ĒÜŹļōØĒĢśļŖö ļ░śļ®┤ņŚÉ ņĄ£ĻĘ╝ņŚÉ Ļ░£ļ░£ļÉ£ ņ¢æņĢł ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØĆ ĒĢśļéśņØś ļīĆņāüņØä ņä£ļĪ£ ļŗżļźĖ Ļ░üļÅäņŚÉņä£ ņ┤¼ņśüĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Fig. 1). ĻĘĖ Ļ▓░Ļ│╝ļź╝ ņĪ░ĒĢ®ĒĢśļ®┤ Ļ░£ņäĀļÉ£ ĒÆłņ¦łņØś ņśüņāüņØä ņ¢╗ņØä ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā, ļ¬©ĒśĖĒĢ£ ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņ×ģņ▓┤ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒīÉļŗ©ņØä ļ¬ģĒÖĢĒ׳ ĒĢśĻ▒░ļéś ļŹö ņĀĢĒÖĢĒĢśĻ▓ī Ēü¼ĻĖ░ļź╝ ņĖĪņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ļō▒ ņ×äņāüņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ£ĀņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ļŹö ļ¦ÄņØ┤ ņ¢╗ņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż(Fig. 2) [9].
ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØä ĒåĄĒĢ┤ ņ¢╗ņØä ņłś ņ׳ļŖö ņ×äņāüņĀüņØĖ ņĀĢļ│┤ļŖö ļŗ©ņł£ ļ│æļ│Ć ņśüņāüņŚÉ ĻĄŁĒĢ£ļÉśņ¦Ć ņĢŖļŖöļŗż. ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāüņØä ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņČöņĀĢĒĢ£ ļ│æļ│ĆņØś ņ£äņ╣ś ņĀĢļ│┤ļŖö ĒøäņåŹ Ļ▓Ćņé¼ļéś ņ╣śļŻī ļ░®ļ▓ĢņØä Ļ▓░ņĀĢĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ņżæņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ļ│äļÅäņØś ņ▓┤ņÖĖ ņä╝ņä£ļź╝ ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņ£äņ╣śļź╝ ņČöņĀĢĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņ£╝ļéś, ļ│ĄĻ░Ģ ļé┤ņŚÉņä£ ņןĻ┤ĆņØś ņøĆņ¦üņ×ä ļĢīļ¼ĖņŚÉ ņ×äņāüņĀü ĒÜ©ņÜ®ņä▒ņØĆ ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢśļŗż[10]. ņ┤¼ņśüļÉ£ ņśüņāüņØä ņ×¼ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢśļ®┤ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņןĻ┤Ć ļé┤ ņØ┤ļÅÖ Ļ▓ĮļĪ£ļź╝ ņČöņĀüĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ│Ā ņØ┤ļŖö ļ│æļ│ĆņØś ņ£äņ╣ś ņČöņĀĢņŚÉ ļÅäņøĆņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļÅÖņŗ£ņĀü ņ£äņ╣śņČöņĀĢ ļ░Å ņ¦ĆļÅäņ×æņä▒ ĻĖ░ņłĀ(simultaneous localization and mapping)ņØĆ ņ┤¼ņśüļÉ£ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ĒśĢņāüĻ│╝ ĻĘĖļ”╝ņ×Éļź╝ ļČäņäØĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ╣┤ļ®öļØ╝ņØś ņ×ÉņäĖņÖĆ ņØ┤ļÅÖ Ļ▓ĮļĪ£ļź╝ ņ×ģņ▓┤ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ĒĢ┤ņäØĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļÅäļĪØ ĒĢ£ļŗż[11,12]. ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ĒŖ╣ņä▒ ņāü ņØĖņĀæĒĢ£ ņśüņāü ņĢłņŚÉļŖö ļÅÖņØ╝ ļīĆņāüņØ┤ ņ┤¼ņśüļÉ£ Ļ▓ĮņÜ░Ļ░Ć ļ¦ÄņØĆļŹ░ ņØ┤ļōżņØä ņ×¼ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņןĻ┤Ć ļé┤ ņ£äņ╣ś ņČöņĀĢņØ┤ Ļ░ĆļŖźĒĢ£ ņ¦ĆļÅä ņ×æņä▒ņØä ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[13].
ņśüņāü ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ Ļ░£ņ▓┤ļź╝ ĻĄ¼ļ│äĒĢśļŖö ņśüņāü ņØĖņŗØ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØś ĒĢ£ ļČäņĢ╝ņØ┤ļŗż. ņØ┤ļŖö ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāü ņĢłņŚÉņä£ ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņ░ŠļŖö ļŹ░ ļÅäņøĆņØä ņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņåīņן ļ│æļ│ĆņØ┤ Ļ░¢ļŖö ņ¦łĻ░É ļō▒ ņśüņāü ĒŖ╣ņ¦ĢņØä ņłśņ╣śĒÖöĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒĢ┤ļŗ╣ ĻĖ░ņżĆņØä ņČ®ņĪ▒ĒĢśļŖö ņśüņāüņØä ņČöļĀżļé┤ļŖö ļ░®ņŗØņØś support vector machineņØä ņØ┤ņÜ®ĒĢśņŚ¼ ņןĻ┤Ć ļé┤ņČ£Ēśł ņåīĻ▓¼ņŚÉņä£ ĒØöĒ׳ ĒÖĢņØĖļÉśļŖö ļČēņØĆ ņāēņĪ░ņØś ĒÖöņåīĻ░Ć ĒāÉņ¦ĆļÉ£ ņśüņāüņŚÉ ņÜ░ņäĀ ņł£ņ£äļź╝ ļæÉĻ▒░ļéś ņ£Āņé¼ļÅäĻ░Ć ļåÆņØĆ ņśüņāüņØä Ļ▒Ėļ¤¼ļé┤ ĒīÉļÅģņ×ÉĻ░Ć Ļ┤Ćņ░░ĒĢ┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢśļŖö ņśüņāüņØś ĻĘ£ļ¬©ļź╝ ņżäņŚ¼ņżä ņłś ņ׳ļŗż[14-19].
ņśüņāü ņØĖņŗØ ļČäņĢ╝ņŚÉņä£ ņØĖĻ│Ąņ¦ĆļŖźņØś ņä▒ļŖźņØĆ ĒĢ®ņä▒Ļ│▒ ņŗĀĻ▓Įļ¦Ø(convolutional neural network, CNN)ņØś ļÅäņ×ģņ£╝ļĪ£ Ēü¼Ļ▓ī Ļ░£ņäĀļÉśņŚłļŗż(Table 1). ņל ļČäļźśļÉ£ ņśüņāüņØä ĒĢÖņŖĄĒĢ£ ņØĖĻ│Ąņ¦ĆļŖźņØĆ ļåÆņØĆ ņåīņן ļ│æļ│Ć ņØĖņŗØļźĀņØä ļ│┤ņśĆņ£╝ļ®░, ĒīÉļÅģņ×ÉņØś ļČĆņĪ▒ĒĢ£ Ļ▓ĮĒŚśņØä ļ│┤ņÖäĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłļŗż[19-24]. ĒĢśņ¦Ćļ¦ī ļīĆļČĆļČäņØś ņŚ░ĻĄ¼Ļ░Ć ļ»Ėļ×Ć, ĻČżņ¢æ ļō▒ņØś ņĀÉļ¦ē ņåÉņāüņØ┤ļéś ņČ£Ēśł, ĒśłĻ┤Ć ĒÖĢņןņ”Ø ļō▒ ņŻ╝ļ│ĆļČĆ ņĀÉļ¦ēĻ│╝ ņל ĻĄ¼ļČäļÉśļŖö ĒśĢņāüņŚÉ ĻĄŁĒĢ£ĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒĢÖņŖĄņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢśņśĆĻ│Ā, ļŗżļźĖ ņØ┤ņāü ņåīĻ▓¼ņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢĀ ņłś ņŚåņ¢┤ ņŗżņĀ£ ņ×äņāüņŚÉņØś ņĀüņÜ®ņŚÉ ĒĢ£Ļ│äĻ░Ć ņ׳ļŗż.
ņåīņן ļ│æļ│ĆņØś ĒŖ╣ņĀĢ ņäĖļČĆ ļČäļźśĻ░Ć ņĢäļŗłļØ╝ ņ×äņāüņĀüņØĖ ĻĄ¼ļ│äņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢ£ņ¦ĆņŚÉ ļö░ļØ╝ ņśüņāüņØä ņ¢æļČäĒĢśņŚ¼ ĻĄ¼ņä▒ĒĢ£ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ĒĢÖņŖĄĒĢ£ ņØĖĻ│Ąņ¦ĆļŖźņØĆ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢ£ ņóģļźśņØś ļ│æļ│ĆņØä ņØĖņŗØĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņŚłņ£╝ļ®░, ļåÆņØĆ ļ│æļ│Ć ņØĖņŗØļźĀņØä ļŗ¼ņä▒ĒĢśĻ│Ā ĒīÉļÅģņŚÉ ņåīņÜöļÉśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ļŗ©ņČĢĒĢśņŚ¼ ĒÜ©ņ£©ņä▒ņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ņØīņØ┤ ņ”Øļ¬ģļÉśņŚłļŗż[25,26].
Ļ▓░ ļĪĀ
ļ░£ņĀäļÉ£ ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ĻĖ░ļŖźņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ļŗżņ¢æĒĢśĻ▓ī ņØ┤ņÜ®ļÉśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØ┤ Ļ░¢ļŖö ĻĖ░ĻĖ░ņĀü ņĀ£ĒĢ£ņĀÉņØä ĻĘ╣ļ│ĄĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ░£ņäĀļÉ£ ĒÆłņ¦łņØś ņśüņāü ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ĒīÉļÅģņ×ÉņŚÉĻ▓ī ņĀ£Ļ│ĄĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØś ņØ┤ļÅÖ Ļ▓ĮļĪ£ļź╝ ņČöņĀüĒĢśņŚ¼ ļ│æļ│ĆņØś ņ£äņ╣ś ņČöņĀĢņŚÉ ļÅäņøĆņØ┤ ļÉĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ņŚ¼ĻĖ░ņŚÉ ĻĖ░Ļ│äņĀüņØĖ Ļ░£ņäĀņØ┤ ļŹö ĒĢ┤ņ¦Ćļ®┤ ļ│æļ│ĆņŚÉ ļīĆĒĢ£ ļŹö ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņ×äņāü ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ ĒÖĢņØĖĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳ļŗż. ļöźļ¤¼ļŗØņØä ĒÖ£ņÜ®ĒĢ£ ņśüņāü ņØĖņŗØ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØĆ ĒīÉļÅģņ×ÉņØś ļ│æļ│Ć ļ░£Ļ▓¼ņ£©ņØä Ē¢źņāüņŗ£ĒéżĻ│Ā ĒīÉļÅģņŚÉ ņåīņÜöļÉśļŖö ņŗ£Ļ░äņØä ņżäņŚ¼ņŻ╝ņ¢┤ ĒÜ©ņÜ®ņä▒ņØä Ļ░£ņäĀĒĢśļŖö ļŹ░ ļÅäņøĆņØ┤ ļÉ£ļŗż.
ņ╗┤Ēō©Ēä░ ļ╣äņĀä ĻĖ░ņłĀņØ┤ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņŚÉ ļ│ĖĻ▓®ņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņĀüņÜ®ļÉśņ¢┤ ņ×äņāüņŚÉņä£ ĒÖ£ņÜ®ļÉśĻĖ░ ņ£äĒĢ┤ņä£ļŖö ļŹö ļ¦ÄņØĆ ļģĖļĀźņØ┤ ĒĢäņÜöĒĢśļŗż. ĒøäĒ¢źņĀüņ£╝ļĪ£ ņłśņ¦æļÉ£ ļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į ņśüņāü ņĀĢļ│┤ļź╝ Ēæ£ņżĆĒÖöĒĢśņŚ¼ ņל ņĀĢļ”¼ļÉ£ ļīĆĻĘ£ļ¬©ņØś ĒĢÖņŖĄ ņ×ÉļŻīļź╝ ĻĄ¼ņČĢĒĢśĻ│Ā Ļ░£ļ░£ļÉ£ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØś ņ×äņāüņĀü ĒÜ©ņÜ®ņä▒ņØä ļ¦ÄņØĆ ņ”ØļĪĆņŚÉņä£ ņ×ģņ”ØĒĢśļŖö ņØ╝ņØ┤ ļÆĘļ░øņ╣©ļÉśņ¢┤ņĢ╝ ĒĢ£ļŗż. ņØ╝ļ░śņĀüņØĖ ņ£ä, ļīĆņןļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņŚÉ ļ╣äĒĢ┤ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØ┤ ņŗ£Ē¢ēļÉśļŖö ļ╣łļÅäļŖö ļ¦żņÜ░ ņĀüņØĆ ĒÄĖņ£╝ļĪ£ ļŗżĻĖ░Ļ┤ĆņØś ĒśæļĀźņØ┤ ĒĢäņłśļŗż. ļīĆĒĢ£ļ»╝ĻĄŁņØĆ ņØśļŻī, Ļ│ĄĒĢÖ ĻĖ░ņłĀ ņäĀņ¦äĻĄŁņØ┤ļ®░ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓Į Ļ┤ĆļĀ© ņøÉņ▓£ ĻĖ░ņłĀņØä Ļ░Ćņ¦ä ĻĖ░ņŚģņØä ļ│┤ņ£ĀĒĢśĻ│Ā ņ׳ļŗż. ņØśņé¼ņÖĆ Ļ│ĄĒĢÖņ×É Ļ░äņØś ņĀüĻĘ╣ņĀüņØĖ ĒśæļĀźņØä ļ░öĒāĢņ£╝ļĪ£ ņ║ĪņŖÉļé┤ņŗ£Ļ▓ĮņØ┤ ļ░£ņĀäĒĢśņŚ¼ ĻĄŁļ»╝ļōżņØś Ļ▒┤Ļ░Ģ ņ”Øņ¦äņØĆ ļ¼╝ļĪĀ, ĻĄŁĻ░Ć Ļ▓Įņ¤üļĀź ĒÖĢļ│┤ņŚÉļÅä ĻĖ░ņŚ¼ĒĢĀ ņłś ņ׳Ļ▓ī ļÉśĻĖ░ļź╝ ļ░öļØ╝ļŖö ļ░öņØ┤ļŗż.



 PDF Links
PDF Links PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Full text via DOI
Full text via DOI Download Citation
Download Citation Print
Print






