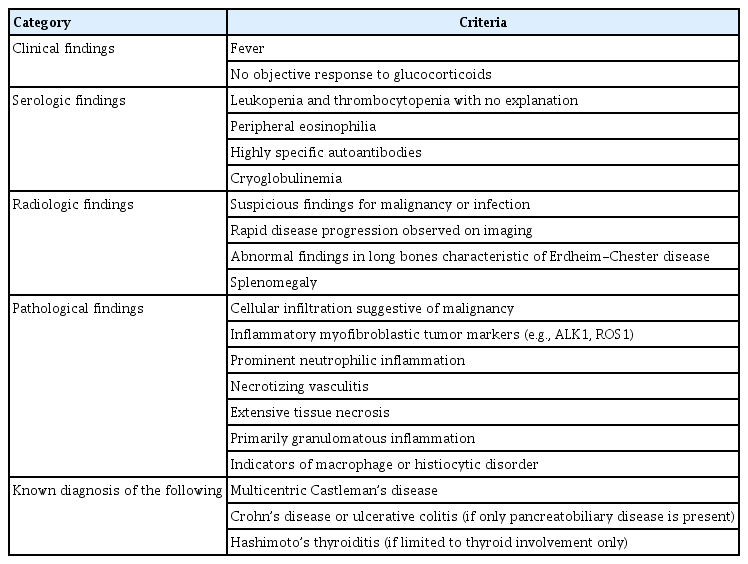
호전과 악화를 반복하는 턱밑샘 비대와 양 눈꺼풀 부종으로 내원한 52세 남자
Recurrent Submandibular Mass and Bilateral Periorbital Edema in IgG4-Related Disease: A Case Report
Article information
Trans Abstract
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is an immune-mediated systemic disorder characterized by inflammatory, proliferative, and fibrotic lesions that can affect any body organ. The severity and extent of organ involvement vary significantly among individuals. Diagnosis of IgG4-RD necessitates a comprehensive assessment, including clinical presentation, radiological findings, laboratory tests, and histopathological examination. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism classification criteria offer a valuable framework for diagnosing IgG4-RD. Although glucocorticoids and rituximab are the primary treatment options, the optimal long-term management strategy for IgG4-RD remains undetermined.
증례: 52세 남자가 약 1년 전 왼쪽 턱밑 부종이 발생하였다. 턱밑 부종은 호전과 악화를 반복하며 좌우를 번갈아 나타났으나 통증이나 압통은 없었다. 약 6개월 전에는 양 눈꺼풀 부종이 나타나기 시작하였고 스테로이드를 4-5일 복용하면 턱밑 부종과 함께 호전되는 양상을 보였다. 그러나 점차 턱밑 부종은 호전 없이 지속되며 덩어리로 만져지고 위, 아래 눈꺼풀 부종와 함께 안구 돌출이 지속되어 내원하였다. 과거력상 고지혈증을 진단받았으나 약물 복용은 하지 않고 있었다.
내원 당시 활력 징후는 혈압 120/70 mmHg, 맥박 86회/분, 호흡 18회/분, 체온 36.5℃였다. 약간의 피로감을 호소하였으나 열감이나 오한, 체중 감소, 근육통이나 관절통을 포함하여 전신적 증상은 없었다. 이학적 검사상 커진 턱밑샘이 촉진되었고 초음파 검사상 커진 턱밑샘과 주변 임파선을 확인할 수 있었다. 턱밑샘에 대해 core needle biopsy를 시행하였고 조직 검사상 chronic lymphoplasmacytic sialadenitis and sclerotic stroma 소견을 보여 턱밑샘에 발생한 immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) 관련 질환 가능성을 의심하였다. 종괴를 형성할 수 있는 다양한 질환들을 배제하고 전신 질환으로써 IgG4 관련 질환이 장기를 침범한 정도를 파악하기 위해 추가 검사들을 진행하기로 하였다.
혈액 검사에서 백혈구 4,180/mm3 (정상, 4,000-11,000; 단핵구, 12.4%; 호산구, 5.0%), 헤모글로빈 14.9 g/dL (정상, 13.8-17.2), 혈소판 257 × 103/mm3 (정상, 150-450), erythrocyte sedimentation rate 13 mm/hr (정상, < 15), C-reactive protein 0.3 mg/L (정상, < 10)였다. 그리고 IgG 1,973 mg/dL (정상, 700-1,600), IgG4 1,260 mg/dL (정상, 3.9-86.4)였다. 자가항체 검사로 시행하였던 anti-nuclear antibody (ANA)와 anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)를 포함하여 anti-Ro, anti-La, anti-double strand DNA (dsDNA), anti-Smith antibodies는 모두 음성이었고 complement 3 (C3)와 C4 수준은 감소되어 있었다. 혈청과 소변의 단백전기영동 검사(protein electrophoresis)에서 비정상 밴드는 관찰되지 않았고 한랭글로불린 음성, lactate dehydrogenase와 소변 검사는 정상 소견이었다.
흉부 X선 검사는 정상이었고 경부, 흉부, 복부 computed tomography (CT)와 positron emission tomography/CT (PET/CT)를 시행하였다. 양측 턱밑샘 외 양측 눈물샘과 비인두, 사골동 및 전립선, 양측 경부 림프절(level IB, II) 및 종격동 림프절(4R, 4L, 7, 9, 10R, 10L, 11R, 11L)에서 크기 증가와 IgG4 관련 질환의 침범이 의심되었다(Fig. 1). 캐슬만병과 림프종을 배제하기 위하여 종격동의 7 lymph node (LN), 11R LN에 대해 endobronchial ultrasound scan (EBUS)을 통해 조직 검사를 시행하였고 해당 가능성은 없는 것을 확인하였다. 전립선 조직 검사로 악성 종양을 배제하고 nodular hyperplasia를 확인하였다.
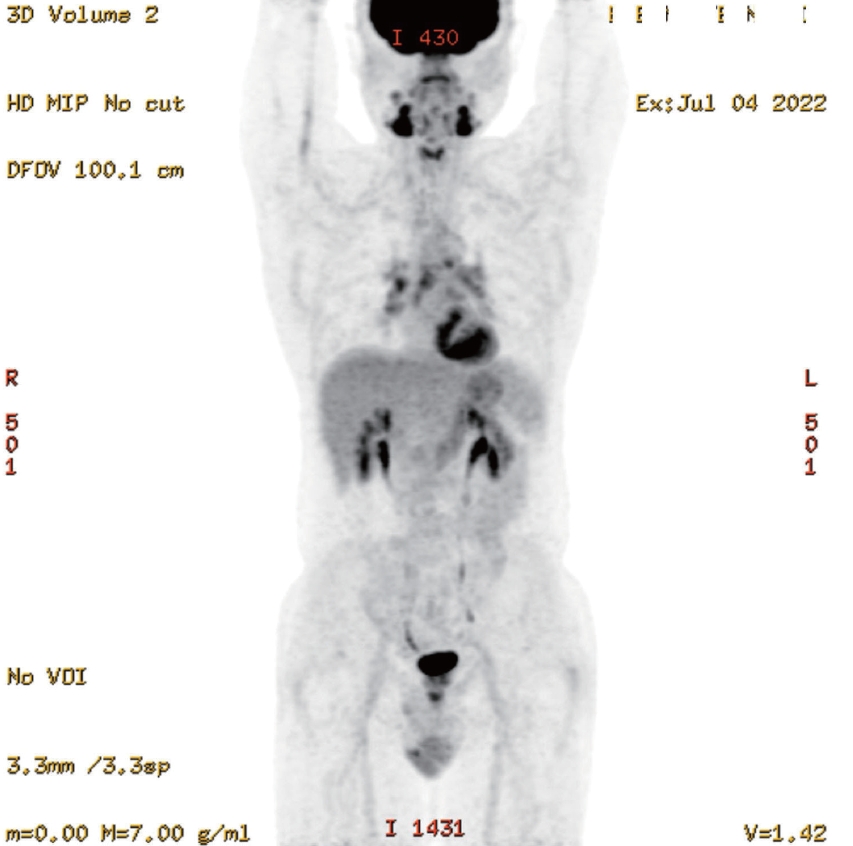
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) body scan of patient. In the whole-body PET/CT scan using 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose (18F-FDG), increased FDG uptake was observed in the bilateral submandibular glands, bilateral lacrimal glands, bilateral nasopharynx, bilateral ethmoid sinuses, prostate, bilateral cervical lymph nodes (level IB, II), and mediastinal lymph nodes (4R, 4L, 7, 9, 10R, 10L, 11R, 11L), suggesting possible involvement of IgG4-related disease in these regions. IgG4, immunoglobulin G4.
IgG4 관련 질환의 병변부에 대한 조직병리학적 평가를 위한 면역 염색 시 형질세포 마커인 CD138 염색이 안된다면 IgG, IgG4에 대한 면역 염색을 진행할 수 없다. 증례 환자의 면역 염색(Fig. 2)에서 충분히 많은 CD138 염색이 확인되어 IgG, IgG4 염색을 진행하였고 조직의 퇴행성 변화가 심하였으나 육안적으로 IgG 양성인 세포가 120개 정도였고 IgG4 양성인 세포가 적어도 100개 이상으로 매우 증가된 것을 확인하여 IgG4 대 IgG4 비율이 71%를 초과한 것으로 확인되었다. 이로써 분류 기준을 따라 최종적으로 IgG4 관련 질환을 분류하였고 환자의 임상 양상과 영상학적, 실험실적, 조직병리학적 소견을 종합할 때 진단에 대한 충분한 근거가 있다고 판단하여 고용량 스테로이드 치료를 시작하였다.
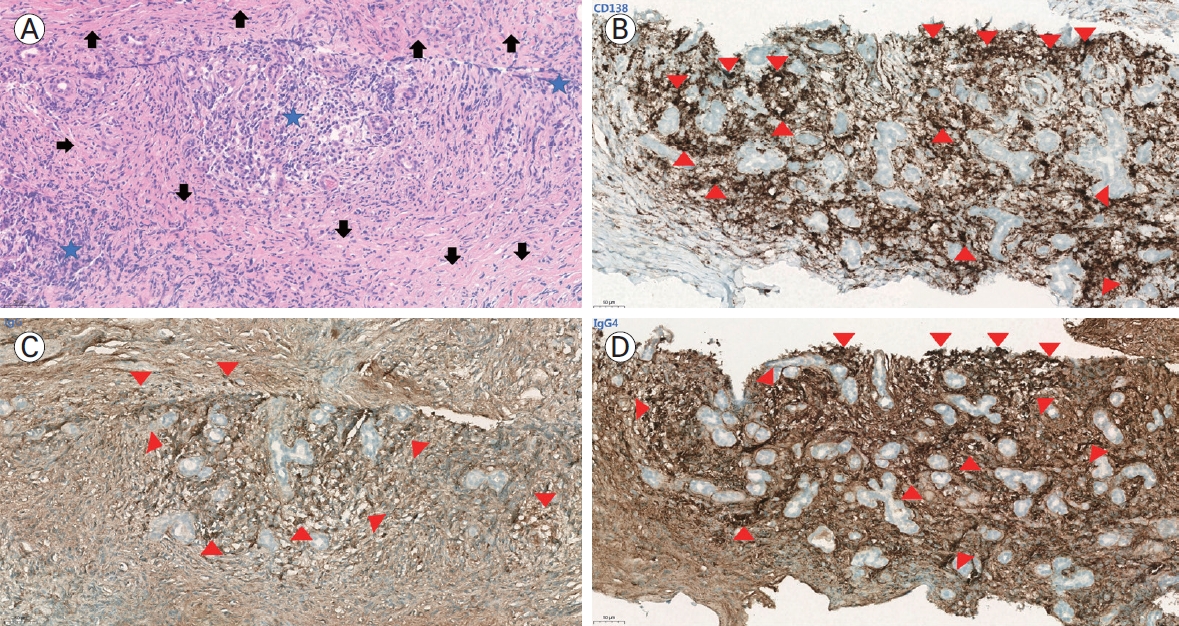
Histopathologic findings of the submandibular gland in the case patient. (A) H&E stain (× 200). (B) CD138 immunohistochemical stain (× 200). (C) IgG immunohistochemical stain (× 200). (D) IgG4 immunohistochemical stain (× 200). Histopathologic analysis of the submandibular gland tissue obtained through core needle biopsy revealed chronic lymphoplasmacytic sialadenitis and sclerotic stroma on H&E staining. Additional immunohistochemical staining for CD138, IgG, and IgG4 demonstrated a marked abundance of IgG4-positive plasma cells and an IgG4/IgG ratio exceeding 71%, consistent with the histopathologic criteria for IgG4-related disease. (A) The H&E stain shows glandular atrophy and sclerosis (arrows) with prominent inflammatory cell infiltration (blue stars) composed mainly of lymphocytes and plasma cells, indicating chronic inflammation. (B) CD138, a plasma cell marker, highlights the gland’s dense population of plasma cells (red arrowheads). (C) IgG immunostaining demonstrates that most of the plasma cells are stained brown, indicating a high proportion of IgG-secreting plasma cells (red arrowheads). (D) IgG4 immunostaining reveals a significant number of plasma cells stained brown, indicating a high proportion of IgG4-secreting plasma cells (red arrowheads). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; IgG, immunoglobulin G.
서 론
IgG4 관련 질환은 거의 모든 장기 또는 해부학적 부위에 염증성, 증식성, 섬유성 병변을 일으키는 면역 매개 전신 질환으로 장기의 침범 정도와 중증도는 매우 다양할 수 있다. IgG4 관련 질환 진단을 위해서는 임상의가 질환이 침범하는 전형적인 부위를 인식하고 임상적, 영상학적, 실험실 검사 소견 및 병변의 조직병리학적 소견을 종합적으로 판단하는 것이 필요하며 여기에는 유사 질환을 배제하는 과정도 포함된다.
본 론
진단의 첫 단계: 진입 기준(step 1: entry criteria)
IgG4 관련 질환은 임상병리학적 진단(clinicopathologic diagnosis)이다. 혈청 IgG4 농도의 상승은 민감하지도 않고 특이적이지도 않으며 질병에서 특징적인 조직병리학적 소견 역시 IgG4 관련 질환과 임상 양상이 겹치는 질환을 포함하여 다양한 다른 상태에서도 관찰될 수 있다[1-3]. 배제 질환을 평가하기 위해서도 조직병리학적 진단 과정은 중요하다. 따라서 적절한 임상 상황에서 영상학적, 실험실적, 조직병리학적 소견을 결합한 종합적 평가를 토대로 진단이 이루어져야 한다.
미국류마티스학회와 유럽류마티스학회가 2019년에 공동으로 승인한 IgG4 관련 질환 분류 기준[4]은 임상 진단을 위한 목적으로 설계된 것은 아니지만 이 기준을 적용할 때 진단에 적합한 접근 방식을 따를 수 있어 유용하다. 가장 먼저 환자는 IgG4 관련 질환에 의한 전형적인 장기 침범을 보여야 하는데 전형적이라 함은 임상적, 영상학적, 또는 조직병리학적으로 전형적인 소견을 나타낼 때 이것이 IgG4 관련 질환 진단을 의심하는 첫 번째 단서가 된다. 전형적이라고 간주되는 장기는 눈물샘, 주요 타액샘, 안와, 폐, 척추 주위 연조직, 췌장, 담도, 신장, 후복막, 대동맥, 뇌막, 갑상선이다. 또는 전형적인 장기 중 어느 하나에서 우연히 조직병리학적으로 원인 불명의 림프형질세포성 침윤을 동반하는 염증 소견을 보인다면 IgG4 관련 질환 진단 과정에 진입할 수 있다. 그러나 조직병리에서 IgG4+ 형질세포는 류마티스관절염이나 ANCA 관련 혈관염, 아토피 피부염 등 다른 질환에서도 증가할 수 있으니 주의가 필요하다.
본 증례의 환자는 주요 타액샘인 턱밑샘과 눈물샘 부종이 호전과 악화를 반복하며 내원하였고 영상 검사에서도 이 부위의 이상을 확인함으로써 전형적으로 간주되는 장기 침범의 근거를 가지고서 IgG4 관련 질환의 진단의 첫 단추를 끼울 수 있었다.
주요 제외 기준(step 2)
전형적인 장기를 침범하는 양상이라고 할 때 환자는 다른 가능성을 시사하는 어떠한 배제 기준도 충족해서는 안 된다(Table 1). 주요 제외 기준 중 하나라도 존재한다면 이미 환자는 IgG4 관련 질환으로 볼 수 없고 이는 강력하게 다른 진단을 고려하여야 한다는 것을 시사한다.
IgG4 관련 질환에서 전신 발열은 드물게 나타난다. 피로감은 주로 다발성 장기 침범 시에 흔히 나타날 수 있고 관절통도 발생할 수 있지만 명확한 관절염 소견이 나타나는 경우는 흔하지 않다.
IgG4 관련 질환을 배제하기 위해 특정 자가항체 검사가 필요하지는 않다. 오히려 진단 과정에서 IgG4 관련 질환을 모방할 수 있는 질환과 연관된 자가항체가 발견되면 IgG4 관련 질환을 배제하는 근거가 될 수 있다. 이렇게 적용할 수 있는 자가항체로는 anti-proteinase 3 (PR3) 또는 anti-myeloperoxidase (MPO)와 같은 ANCA, anti-Ro 및 anti-La 항체, anti-dsDNA antibody와 같은 전신 홍반 루푸스에 특이도가 높은 혈청 검사 등이 있다. ANA, 항인지질항체(antiphospholipid antibody), 평활근항체(anti-smooth muscle antibody) 또는 미토콘드리아항체(anti-mitochondrial antibody)와 같이 특이도가 낮은 항체로는 IgG4 관련 질환을 배제하지 못한다.
조직병리학적으로 종종 호산구 침윤이 보일 수 있으나 호중구 침윤은 전형적인 소견이 아니다. 대식세포 또는 조직구 질환의 지표 중 하나의 예로 Rosai-Dorfman병에서 관찰되는 S100-양성 대식세포가 있으며 이는 엠페리폴레시스(emperipolesis)를 나타낸다.
오직 췌장담도 질환만 있는 경우에 기저 질환으로 염증성 장질환이 동반되어 있는 환자라면 이는 IgG4 관련 질환으로 분류할 수 없다. IgG4 관련 질환 환자에서 하시모토 갑상선염이 병발될 수 있으나 갑상선 단독으로 침범된 환자를 평가할 때 하시모토 갑상선염이 있다면 IgG4 관련 질환을 배제하여야 한다.
본 증례의 환자는 피로감 외에 발열이나 뚜렷한 전신 증상이 없었고 본격적인 진단과 치료 전에 투여되었던 글루코코르티코이드에 반응하였던 병력을 확인할 수 있었다. 내원 후 혈액 검사상 백혈구 감소와 혈소판 감소, 호산구 증가 및 한랭글로불린의 존재는 없었다. 특이도가 높은 자가항체와 연관된 해당 자가면역 질환의 임상 양상도 없었지만 특이 항체들 역시 음성이었다. 기저 질환으로 배제가 필요한 질환은 없었으나 두경부와 흉부에서 다수 관찰된 림프절 병증에 대해 다초점 캐슬만병과 림프종을 배제하는 조직학적 진단과 IgG4 관련 질환에서 비전형적인 장기인 전립선 이상에 대하여 악성을 배제하기 위한 조직학적인 진단 과정을 진행하였다. 전형적인 침범 장기인 턱밑샘에서 시행하였던 조직 검사와 면역 염색에서 병리학적으로 배제가 필요한 소견은 보이지 않았다.
진단의 마지막 관문(step 3)
분류 기준을 이용해서 진단을 도출한다고 할 때 가장 마지막 단계는 분류 기준에 제시된 가중치에 따라 점수를 적용함으로써 최종 점수를 도출하는 것이다(Table 2). 이렇게 따라가는 일련의 과정을 통해 임상의는 IgG4 관련 질환을 환자의 진단으로 고려하는 것이 적절한지에 대한 가이드를 얻을 수 있다.
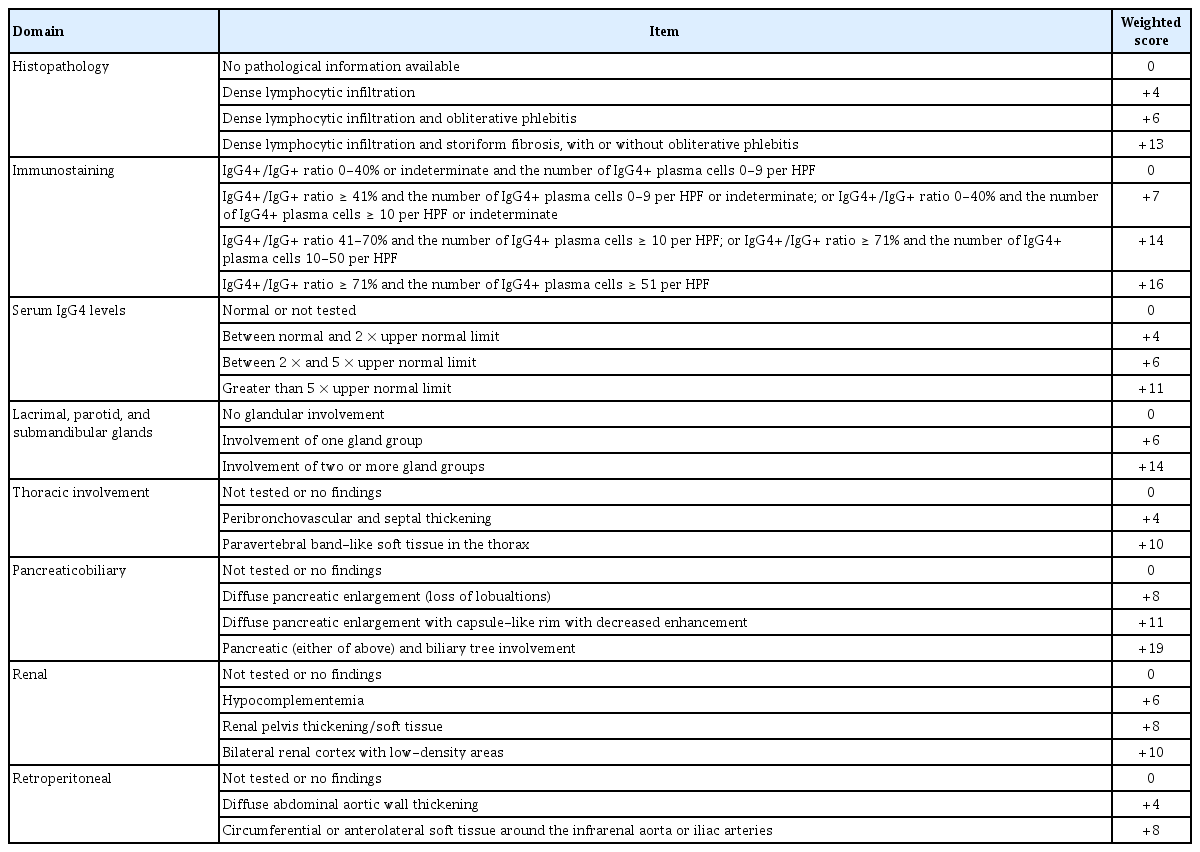
마지막 단계에 오면 각 카테고리에서 가장 높은 가중치 항목 하나만 셈에 포함되는데 가중치의 총합이 20점 이상이면 IgG4 관련 질환으로 분류가 가능하다. 가중치를 셈하는 데 있어 중요한 것 중 하나는 림프절과 위장관 점막 그리고 피부에서 이루어진 조직 검사는 면역 염색 카테고리 가중치로 받아들여지지 않는다는 점이다. 특히 면역 염색에서 판정 불가능이란 의미는 병리학자가 침윤 내 양성 염색 세포의 수를 정확히 셀 수는 없지만 그 수가 최소한 고배율 시야당 10개 이상임을 확인할 수 있는 상황을 의미하는데 이는 주로 면역 염색의 품질 문제로 인하여 발생한다. 이러한 경우에도 병리학자는 적절한 면역 염색 결과 범주로 사례를 분류할 수 있다.
증례의 환자가 양측 턱밑샘과 눈물샘 부종을 호소하였고 이는 IgG4 관련 질환에서 전형적인 침범 장기로 합당하였기에 진단의 첫 단추를 끼울 수 있었다. 동시에 주요 제외 기준 중 어느 것도 충족하지 않은 상태로 확인되어 진단의 마지막 관문에 이를 수 있었다. 이제 가중치 점수를 더해 본다고 하면 병리 소견상 폐쇄성 동맥염이나 소용돌이 섬유화 없이 조밀한 림프구 침윤만 있고 침샘 조직에서 시행한 면역 염색에서 IgG4+와 IgG+ 비율이 71%를 초과하고 IgG4+ 세포 수가 100개 이상으로 확인되어 각각 4점과 16점을 획득하였고 혈청 IgG4 농도가 정상의 5배 이상으로 11점, 양측 눈물샘과 귀밑샘과 턱밑샘을 침범하여 14점, 보체 감소가 확인되어 6점으로 총합 51점이 확인되었다. 증례의 환자에서 림프절 조직병리 소견은 가중치 판단에 포함되지 않았고 임상 상황과 영상학적, 조직병리학적 소견을 종합적으로 판단하여 IgG4 관련 질환으로 진단이 가능하였다. 임계값 20을 기준으로 IgG4 관련 질환 분류 기준의 검증 코호트에서 여러 민감도 분석을 시행하였을 때 민감도 83%, 특이도 98.9%로 매우 우수한 성능을 보이는 것이 확인되었다[4].
결 론
IgG4 관련 질환은 2003년에 전신 질환 개념으로 정립되었다[5,6]. 이후 지식의 놀라운 발전에도 불구하고 그 원인은 여전히 명확하지 않으며 최근 다양한 크기의 혈관을 침범하는 양상이 확인되어 질환의 병태생리로서 혈관염 가능성이 제시되기도 하였다[7]. IgG4 관련 질환은 재발-완화의 패턴을 가지고 수개월에서 수년에 걸쳐 장기에 돌이킬 수 없는 손상을 축적하여 동반 질환과 사망률을 증가시킬 수 있을 것으로 생각된다. 따라서 조기 진단과 신속한 치료 시작은 단기적으로 좋은 치료 결과를 얻을 가능성을 높여준다. 그럼에도 진단된 모든 환자에서 통상적으로 치료를 시작하는 것은 아니며[8] 대부분의 환자가 장기간 유지 요법이 필요하고 저용량 유지 치료 중 또는 치료 중단 후 25-50% 환자가 재발을 경험한다고 알려져 있다. 현재까지는 글루코코르티코이드와 리툭시맙이 IgG4 관련 질환의 가장 확립된 치료 방법이며 이 질환의 장기 관리에 대한 최적의 접근법은 여전히 연구 중이다[9,10]. IgG4 관련 질환 진단에는 임상 소견, 영상 검사, 조직병리, 혈청 검사를 포함한 종합적인 평가가 필요하며 2019년 미국류마티스학회/유럽류마티스학회 분류 기준이 이를 위한 유용한 지침이 될 수 있다.
Notes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
FUNDING
None.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Jiwon Hwang conceptualized and prepared the case report, performed the literature review, drafted the manuscript, and managed all aspects of editing and submission. Yeon-Ah Lee and Seung-Jae Hong critically reviewed the manuscript and provided valuable feedback. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank Prof. Hyoun Wook Lee from the Department of Pathology at Samsung Changwon Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University, for his valuable assistance and expertise in this study.