어린선 환자에서 발생한 혈관면역모세포 T세포림프종 1예
A case of angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma in a patient with ichthyosis
Article information
Abstract
혈관면역모세포 T세포림프종은 비호지킨림프종의 약 1~2%를 차지하는 드문 질환으로, 피부 병변과 과감마글로불린혈증 또는 용혈성빈혈, 흉수와 복수 등을 자주 동반하는 것으로 알려져 있다. AITL에 흔히 동반되는 피부질환은 홍반성판 또는 결절이나 구진의 형태로 나타나며 조직검사상 악성 림프종 세포들의 침윤을 볼 수 있다. 어린선은 전신적인 피부의 과각화증을 보이는 질환으로 유전적 혹은 후천적 경우가 있으며 유전적인 경우가 대부분이다. 저자들은 유전성으로 추정되는 어린선과 자가면역성용혈성빈혈을 동반한 AITL의 두 가지 드문 질환이 병발한 증례를 보고한다.
Trans Abstract
Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL), which accounts for only 1~2% of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, is commonly accompanied by skin lesions. Those associated with AITL include erythematous plaques, nodules or rashes. Histological examination of most lesions shows infiltration by malignant lymphocytes. Ichthyosis is a generalized skin disease characterized by hyperkeratosis, in which the skin acquires an appearance resembling fish scales. Some cases may be acquired, but most have a genetic basis. We report a case of AITL with associated ichthyosis that is considered to be inherited. (Korean J Med 79:206-209, 2010)
서 론
혈관면역모세포 T세포림프종(Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma, AITL)은 비호지킨림프종의 약 1~2%를 차지하지만1) 성숙 T세포림프종 중에서는 15~20%를 차지하는 질환이다. 림프절 구조의 부분적인 소실 및 다형 세포 침윤과 혈관 증식이라는 조직학적 소견을 나타내고, 주로 중년층 이상에서 나타나며, 전신적인 림프절 종대, 간비종대 및 발열과 피부병변 등의 임상상을 나타내며 빈혈, 호산구 증가, Coombs’test 양성 및 고감마글로불린혈증 등의 면역학적 이상을 동반하는 특징을 보인다2). 5년 생존율 30~35%, 중앙생존기간 36개월 미만으로 비호지킨림프종의 다른 아형에 비해 불량한 예후를 보이는 질환이다3-5). 과거에 증후군으로 분류되다가 최근에서야 면역조직화학염색법이 발전하면서 진단이 가능해진 질병으로 그 치료방법과 임상양상에 있어서 아직 밝혀지지 않은 점이 많다.
어린선은 물고기를 의미하는 그리스어 ‘ichthys’에서 유래된 명칭으로 전신에 인설(scale)을 보이는 질환을 총칭하는 질환군이다. 유전적인 것과 후천적인 것이 있으며 유전적인 것 중 가장 흔한 것은 심상성 어린선이며 주로 사지와 체간의 신전면 표피가 과각질화되어 피부가 물고기 비늘 모양으로 보인다. 후천적 어린선의 피부 모양은 심상성 어린선과 유사하며 림프종을 비롯한 여러 암과 갑상선기능저하증, 유전분증, 홍반성루푸스나 피부근염과 같은 자가면역질환, 후천성면역결핍증, 약제 등과 연관되어 발생할 수 있다6).
저자들은 심상성 어린선을 앓고 있는 환자에서 자가면역성용혈성빈혈을 동반한 혈관면역모세포 T세포림프종이 발병한 증례를 경험하였기에 보고하는 바이다.
증 례
환 자: 54세, 남자
주 소: 기침, 발한 및 열감
현병력: 내원 1년 전부터 간간이 생겼다 사라지는 하지 부종 있었고, 최근 2개월 전부터 상기 주소가 발생하여 타 병원 내원하여 4주간 치료받았으나 호전 없었음.
과거력: 유아기에 진단받은 어린선 이외의 특이과거력 없음.
가족력: 여동생(류마티스성 관절염), 이종사촌(어린선)
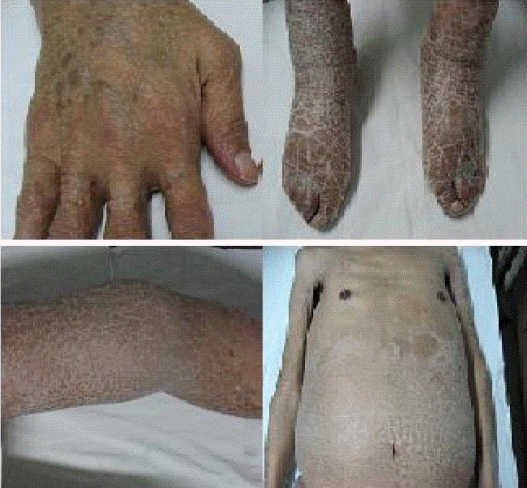
진찰 소견: 내원 당시 혈압 130/80 mmHg, 맥박수 100회/분, 호흡수 32회/분, 체온 38.5℃였고, 흉부 청진상 오른쪽 폐야에 수포음과 전신 피부의 과각화증(그림 1), 양측 하지 부종 및 양측 서혜부에 동통이 없는 다수의 림프절 종대가 촉지되었다.
검사실 소견은 총 백혈구 수 7,000/μL, 헤모글로빈 6.5 g/dL, 혈소판 수 318,000/μL로 빈혈이 있었고, 직접 및 간접 Coombs’ 검사상 용혈 소견을 보였다. AST/ALT/ALP와 BUN/Cr은 정상, 총 단백/알부민 4.7/1.9 g/dL로 감소, CRP는 7.52 mg/dL, 베타2마이크로글로불린은 6.74 mg/L로 상승되어 있었다. 혈장단백전기영동검사상 다클론성 고감마글로불린혈증 소견이 보였다. 골수검사상 세포충실도는 40~50%였고, relative erythroid hyperplasia 외에는 특이소견 없었고, 림프종 세포의 침범은 없는 것이 확인되었다. EBV-VCA IgG 양성, EBV-VCA IgM 음성, EBNA IgG 양성 소견을 보였다.
흉부 컴퓨터촬영 소견상 기관지와 혈관주위 심한 침윤이 있었고, 소엽사이막의 불규칙한 비후가 관찰되었다. 상부 기관지주위림프절과 혈관주위림프절의 다발성 종대(적색 화살표)가 있고, 우측 흉수가 동반되어 있었다(그림 2).

Chest CT image showed diffuse and extensive peribronchovascular infiltration, irregular interlobular septal thickenings, and patchy airspace consolidation, pleural effusion in right side, and bulky mediastinal and prevascular lymphadenopathy.
복부 컴퓨터촬영 소견(그림 3)상 양측 대동맥주위 림프절과 장골동맥주위 림프절 및 서혜부 림프절의 다발성 종대(적색 화살표)가 있었으며 간비종대가 동반되어 있었다.

Multiple conglomerated lymphadenopathy in both inguinal area and both paraaortic area was seen in abdominopelvic CT.
병리 소견: 양측 서혜부 림프절 조직의 PAS 염색상 다형성의 림프구 침윤과 현저한 모세혈관 발달이 관찰되었고, 일부에서 Reed-Sternberg cell과 유사한 세포들이 보인다. CD21 염색 양성으로 여포수지상세포의 수지상 돌기들이 보이며 CD3 염색상은 음성으로 AITL로 진단되었다(그림 4).

Microscopic findings of inguinal lymph node (×400). Polymorphous lymphocytes infiltration and prominent arborizing blood vessel were seen in PAS stain. Processes of follicular dendritic cells were visualized in CD21 stain. CD3 stain showed negative reaction.
치료 및 경과: 진단 당시 병기 4기, IPI 점수는 4점으로 고위험군에 해당하였다. AITL에 대해 복합항암화학치료(Cyclophosphamide, Hydroxydaunomycin, Oncovin, Prednisone)를 2008년 5월 26일부터 2009년 1월 5일까지 6주기 시행하고 부분 관해 소견을 보였고, 림프종의 호전과 함께 용혈성빈혈도 호전을 보였다.
이후 복강 및 흉강 내의 림프절 종대와 폐 침윤이 다시 진행하는 소견을 보이며 전신상태 악화 중 폐렴에 의한 패혈증으로 2009년 1월 21일 사망하였다.
고 찰
AITL의 기본병인은 T세포 유전자의 결함에 의한 면역조절 기능의 이상으로 B세포의 증식을 일으키는 것으로 알려졌다. 이러한 면역 조절 기능의 결함의 원인은 밝혀지지 않았으나, 항원 자극이 림프구 증식을 유발시키리라는 가설이 받아들여지고 있다. 바이러스와 같은 감염체가 선택적으로 면역조절 기능을 파괴하여 이러한 질환을 초래할 수 있는 것으로 알려졌다7). AITL의 임상증상은 림프절 비대, 간비종대, 발열, 발진, 혈청단백 양적 변화 등으로 알려져 있고, 조직학적으로 림프절 구조의 파괴와 소혈관 증식, 다형세포 침윤 등이 특징적인 것으로 알려져 있다. 골수, 폐, 신장, 간, 비장 그리고 소화기에 이환될 수 있으며, 약 50%에서 피부발진을 보인다8). 이 중 피부 병변은 반구진성 또는 구진결절성 발진, 전신적인 점출혈, 홍색부종, 판 등의 다양한 소견을 나타내며 전형적인 조직학적 소견이 없어 양성 염증성 피부질환이나 교원성 질환의 피부소견과 감별이 어려운 것으로 알려져 있다2). 치료 방법으로는 복합항암화학요법이 추천되고 있으며 CHOP (Cyclophosphamide, Hydroxydaunomycin, Oncovin, Prednisone), COPBLAM-V (Cyclophosphamide, Oncovin, Prednisolone, Bleomycin, Adriamycin, Procarbazine), IMEP(Ifosfamide, Methotrexate, Etoposide, Prednisolone), CVP (Cyclophosphamide, Vincristine, Prednisone) 항암제가 치료제로 선택되며 전체 반응률은 50% 정도, 5년 생존율은 28% 정도로 알려져 있다2).
어린선은 전신적인 피부의 과각화증을 보이는 질환으로 유전적 혹은 후천적 경우로 구성된다6,9,10). 심상성 어린선이 가장 흔하여 전체의 95% 정도를 차지하며 filaggrin이라는 keratohyalin 합성의 중요한 구성 요소의 전구체인 profilaggrin을 encoding하는 유전자의 변이에 의해 발생하는 것으로 알려져 있으며 상염색체 우성으로 유전되어 대개는 생후 3개월~1년 이전에 피부병변이 나타나기 시작하여 영아기에 진단된다6,11). 후천적 어린선은 다발성골수종, 림프종양구진증, 호지킨병, 균상식육종, 비호지킨림프종 등의 림프구증식성 질환뿐만 아니라 여러 악성 질환의 동반 피부 병변으로 나타날 수 있다6,12,13).
AITL과 흔하게 동반되는 피부 병변은 반점성구진성 판 또는 결절성 병변으로 조직검사상 다형성 림프구의 혈관주위 침윤을 보이는 것이 대부분이다14,15). AITL에서 림프종세포의 직접침윤 없이 동반되는 피부 병변은 중독성표피괴사융해(toxic epidermal necrolysis) 외에는 보고된 바 없다. 후천성 어린선에 림프종이 동반되는 경우는 미분화거대세포림프종의 증례가 보고된 바 있다13).
증례는 림프절 종대, 간비종대, 발열, 혈청단백 양적 변화와 Coombs’검사 양성의 용혈성 빈혈 등 지금까지 알려진 비교적 전형적인 AITL의 임상특성을 보였다. 증례의 어린선이 후천적보다는 유전성으로 의심되기는 하지만 어린선과 림프종이 동반된 증례보고는 찾기 어렵고, AITL과 어린선이라는 두 가지 흔히 접하기 힘든 질환이 동시 발병한 증례를 경험하게 되어 보고하였다.