폐암 치료 후 발생한 기관지 침범 Mycobacterium intracellulare 감염 1예
Endobronchial Involvement of Mycobacterium intracellulare in a Patient with Previously Treated Lung Cancer
Article information
Trans Abstract
The incidence of nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease is increasing, and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) is the most common causal species. Patients with underlying structural lung disease or an immunosuppressive condition are at increased risk for MAC infections. Endobronchial lesions caused by MAC infection are extremely rare, especially in immunocompetent hosts. Here, we describe a case of a 58-year-old woman with pulmonary infiltration and endobronchial involvement caused by MAC. The patient had shortness of breath and a productive cough. She had undergone surgery and chemoradiotherapy for lung cancer 10 years prior. Radiological findings revealed small centrilobular nodules with consolidation in the right lung and mild stenosis at the right main bronchus. Bronchoscopy revealed yellowish-white caseous necrosis in the right main bronchus. Mycobacterium intracellulare was identified in bronchial washing fluid. She was treated with antimicrobial medications. After 6 months of treatment, bronchial lesions, radiological findings, and symptoms had improved remarkably and she showed culture conversion.
서 론
비결핵 항산균(nontuberculous mycobacteria, NTM)은 폐질환 및 림프절염, 피부 질환 등을 일으킬 수 있으며, 후천성면역결핍증후군과 같이 심한 면역저하 상태일 경우 파종성 질환으로 발병할 수 있다[1]. 국내 NTM 폐질환의 원인 균주를 조사한 이전 연구를 종합하면 Mycobacterium avium complex(MAC)가 가장 많은 원인을 차지하며, 두 번째로 M. abscessus complex, M. kansasii 순이었다[2]. NTM 폐질환의 경우 “섬유 공동형”과 “결절 기관지확장증형”으로 잘 알려진 2가지 임상형태가 있으나, 기관지를 침범한 경우는 정상 면역 성인뿐 아니라 면역저하자 모두에서 극히 드물다[1,3]. 국내에서 면역 정상 환자의 기관지 침범 NTM 사례는 현재까지 3예가 알려져 있다. 저자들은 10년 전 폐암에 대한 수술 및 항암·방사선 치료 후 완전 관해 상태로 경과 관찰 이외의 특이 병력 없는 여자가 수개월간의 기침 및 호흡곤란으로 내원하여 검사 상 M. intracellulare에 의한 기관지 침범이 있는 NTM 폐질환을 진단하고 성공적으로 치료한 사례를 경험하여 문헌 고찰과 함께 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
환자: 58세 여자
주소: 수개월간의 기침 및 가래
현병력: 폐암 치료 후 정기적인 추적 관찰을 위해 서울성모병원 종양내과 진료 중이었으며 내원 6개월 전부터 기침 및 화농성 객담이 지속되어 호흡기내과로 의뢰되었다.
과거력: 내원 14년 전 폐암(adenocarcinoma)으로 타 병원에서 우하엽 절제술과 우상엽 쐐기절제술 및 보조항암요법을 시행 받았다. 내원 10년 전 폐암 재발이 확인되어 우중엽에 사이버 나이프 치료와 보조항암치료를 받았으며, 이후 재발의 증거 없이 완전 관해 상태로 정기적 추적 관찰 중이었다. 또한 40년 전 림프절 결핵으로 1년간 항결핵제 복용 후 완치된 기왕력이 있었다.
사회력: 비흡연자였으며, 농업 종사자였다.
진찰 소견: 내원 당시의 활력징후는 혈압 120/80 mmgHg, 맥박수 88회/분, 체온 37.0℃였고 흉부 진찰 상 우측폐야 후방에 천명음과 악설음이 청진 되었다. 경부림프절 종대 및 액와 림프절 종대는 확인되지 않았다.
검사실 소견: 말초혈액검사 상 백혈구 4,790/mm3 (호중구 50.3%, 림프구 42.6%, 단핵구 6.1%), 혈색소 12.4 g/dL, 혈소판 183,000/mm3로 특이 소견은 없었다. 간기능 및 신장 기능 검사는 정상이었고, C-반응성 단백질 0.17 mg/dL (참고치 < 0.5 mg/dL), 적혈구 침강 속도는 23 mm/h (참고치 0-20 mm/h)로 다소 증가되어 있었다. Anti-human immunodeficiency virus(HIV) 항체는 음성이었다. 객담 항산균 도말 검사는 양성(1+), 결핵균 중합 효소 연쇄 반응은 음성이었다.
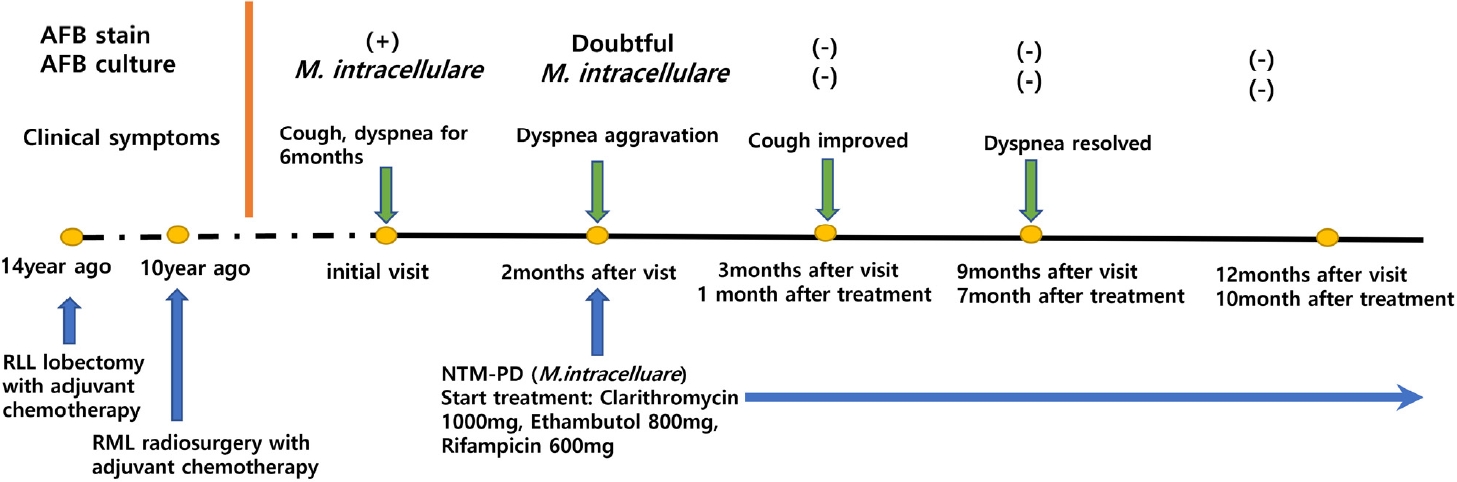
방사선 소견: 내원 당시 단순 흉부 X선 사진에서 우상엽의 경화 및 기존 우하엽 절제술로 인한 용적 감소 소견이 확인되었다(Fig. 1A). 흉부 전산화단층촬영 검사에서 폐암 수술 후 변화로 인한 우측 주기관지의 경도 협착 소견과 더불어 우상엽과 우중엽에 경화와 다발성의 중심소엽성 결절이 확인되었다(Fig. 1B).
(A) Chest X-ray at the initial visit showed infiltrations in the upper right lung field and volume loss of the right lower lung. (B) Chest computed tomography showed multiple small centrilobular nodules with consolidation in the right upper and middle lobes, and mild stenosis of the right main bronchus due to postoperative change.
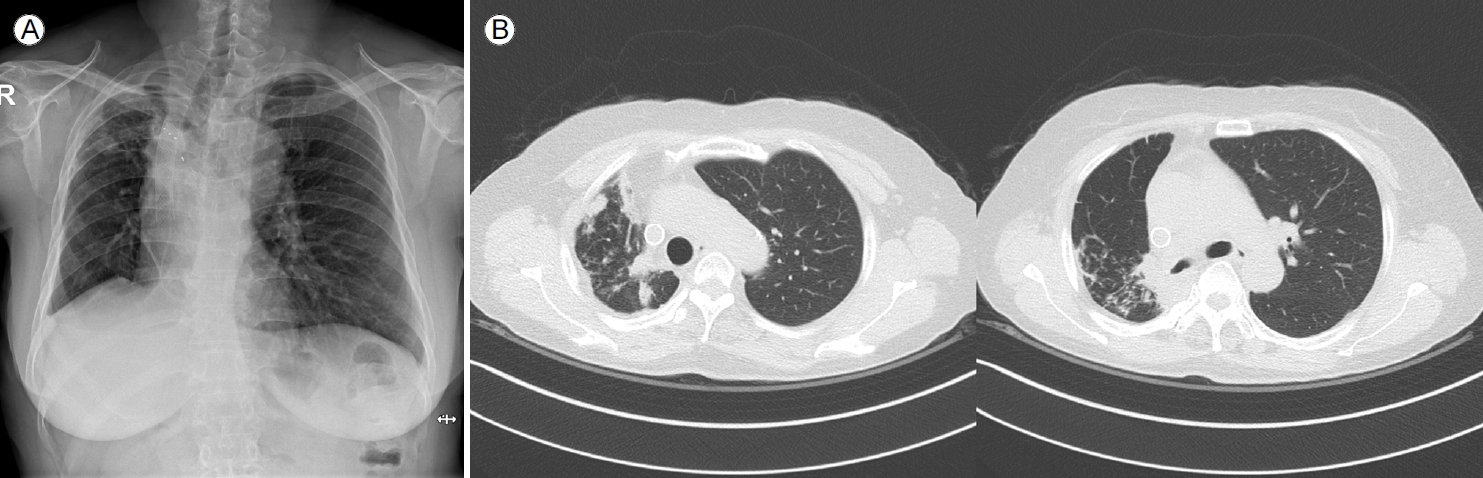
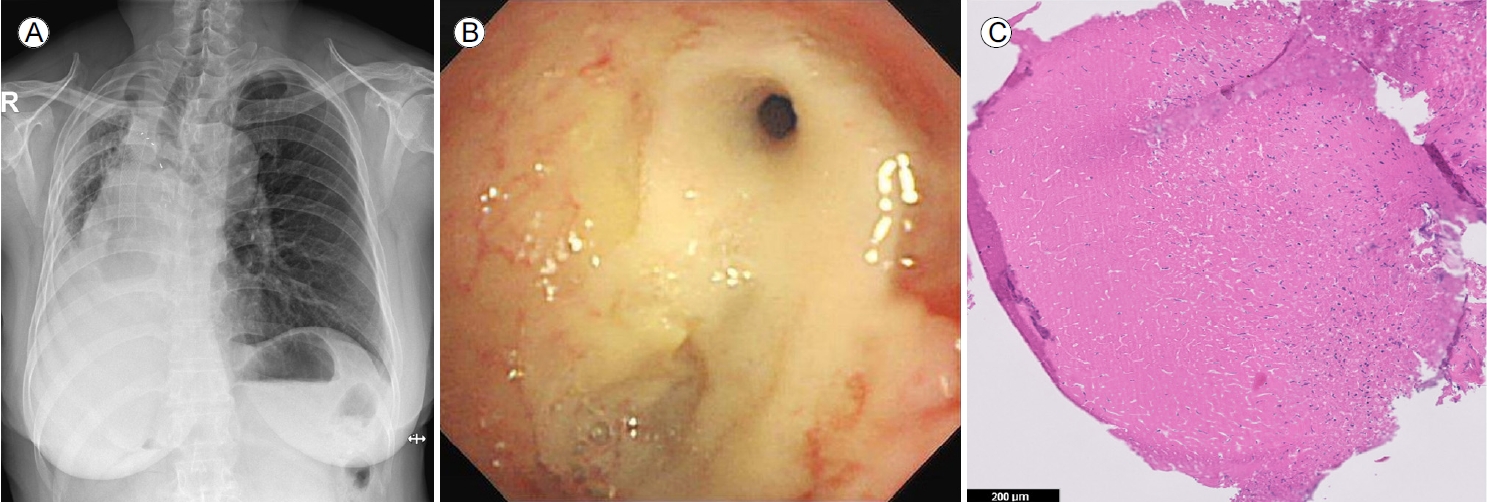
임상 경과 및 치료: 객담 항산균 배양 검사에서 NTM 균이 배양되었고, MAC의 일종인 Mycobacterium intracellulare로 확인되었다. 약제 감수성 검사에서는 clarithromycin에 감수성, amikacin 내성을 보였다. 임상적 증상과 방사선학 검사 및 미생물학 검사 결과를 종합하였을 때 비결핵 항산균 폐질환에 합당하였으나, 증상이 심하지 않아 진해 거담제 투약 및 위식도 역류 대증 치료를 시행하며 경과 관찰하기로 하였다. 환자는 외래 추적 2개월째 기침 및 호흡곤란 악화를 호소하였으며, 흉부 X선 검사 상 폐 허탈로 추정되는 우측 하부 폐야의 음영 증가 소견(Fig. 2A)을 보여 기관지 내시경 검사를 시행하였다. 기관지 내시경 검사 상 우측 주기관지의 충 혈과 유백색을 띤 다량의 건락성 물질이 관찰되었고, 기관지 내강의 협착으로 인해 우상엽 기관지로 진입이 불가능 하였다(Fig. 2B). 기관지 세척액 그람 염색 및 세균 배양 검사상 음성, 항산균 도말 검사 상 양성 의심(doubtful), 결핵균 중합 효소 연쇄 반응 검사는 음성이었다. 기관지경 세포진 검사는 괴사 및 잔여 백혈구 등이었으며 조직 검사 결과 또한 대부분 괴사 조직으로 보고되었다(Fig. 2C). 조직 검체로 시행한 결핵균 중합 효소 연쇄 반응 검사 음성, 비결핵 항산균 중합 효소 연쇄 반응 검사는 양성이었고, 이후 기관지 세척액 배양 검사에서 NTM 배양이 확인되었다. 이전 객담 배양 검사 상 M. intracellulare가 동정되었음을 고려하여 기관지를 침범한 MAC에 의한 NTM pulmonary disease로 진단하였고 ethambutol 800 mg, clarithromycin 1,000 g, rifampin 600 mg 3제 매일 요법 치료를 시작하였다. 2개월 뒤 기관지 세척액에서 배양된 균주는 M. intracellulare로 최종 분리되었다. 이후 한 달 간격으로 객담 항산균 배양 검사를 시행하였고, 치료 1개월 째부터 M. intracellulare는 음전되었다. 약제 치료 7개월 경과 시점에서 기관지 내시경 검사를 하였고 이전과 비교하여 우측 주기관지의 건락 괴사 물질의 뚜렷한 감소가 관찰되었으며 우측 중간 기관지의 입구를 확인할 수 있었다(Fig. 3C). 약물 치료 10개월 경과 후 흉부 방사선 사진(Fig. 3A)에서 기존에 보이던 우측폐야 침윤의 호전을 확인하였으며, 흉부 단층촬영에서도 우상엽의 경화 및 다발성 중심소엽성 결절들이 줄었음을 확인하였다(Fig. 3B). 환자의 임상경과를 요약하면 그림 4와 같다. 환자의 폐기능은 치료 시작 당시 FVC 1.66 L (50%), FEV1 1.28 L (48%) FEV1/FVC 77%에서 치료 시작 12개월째 FVC 2.06 L (63%), FEV1 1.39 L (54%) FEV1/FVC 67%로 폐기능이 다소 호전되었다. 환자는 특별한 약제 부작용 없이 1년 동안 치료 유지하면서 외래 추적 중이다.
(A) Two months after the initial visit, radiography of the chest revealed increased opacity in the right lower lung field. (B) Bronchoscopy revealed a large amount of yellowish-white caseous necrotic material in the right main bronchus. (C) Bronchoscopic biopsy specimens showed caseous necrosis with histiocyte infiltration (hematoxylin and eosin stain, ×100).
(A) Chest X-ray taken 10 months after drug treatment showed improvement of infiltration in the right lung field. (B) Chest computed tomography showed regression of centrilobular nodules and consolidation in the right upper and middle lobes. (C) Bronchoscopy performed after 7 months of treatment showed a marked decrease in caseous necrosis in the right main bronchus.
고 찰
국내에서 결핵의 발병률은 감소하고 있는 반면, 비결핵항산균 폐질환은 현저히 증가하는 추세이다[2,4,5]. 국내 NTM 폐질환의 원인 균주로는 MAC, M. abscessus complex, M. kansasii가 순서대로 주요한 병원체로 보고되었으며, NTM 폐질환은 만성 폐쇄성 폐질환, 기관지 확장증, 결핵의 과거력, 낭포성 섬유증, 진폐증 등 구조적 폐질환이 있는 경우 발병 위험도가 증가하는 것으로 알려져 있다[1,2]. MAC와 연관된 폐질환의 주요 임상상은 상엽 공동형과 결절성 기관지 확장증 2가지 형태가 대표적인데, 본 증례의 경우 비흡연 여성인 점과 흉부 전산화단층 사진 소견을 볼 때 결절성 기관지 확장형에 해당하며 기관지 내 침범을 함께 동반하였다고 볼 수 있다.
결핵으로 인해 유발되는 기관지 결핵과 달리, 비결핵 항산균감염으로 인한 기관지 침범 증례는 매우 드문 것으로 알려져 있다. HIV 항체 양성 환자 및 조혈모세포 이식 기왕력 등 숙주의 면역이 저하된 경우에서 보고된 증례들이 있으나[3,6,7], 점차 면역적격자에서도 발병이 증가하고 있다. 면역적격자의 기관지 침범형 NTM 폐질환은 국외 증례의 경우 MAC 및 Mycobacterium kansasii에 의한 발병 사례들이 확인된 바 있으며[8,9], 국내의 경우 면역적격자에서 기관지를 침범한 NTM 폐질환은 지금까지 총 3건의 증례가 보고되었고 모두 MAC에 의한 감염이었다[10-12]. 첫 보고 증례는 좌측 주기관지 협착과 무기폐를 동반한 형태로, 원인 균주는 M. avium이었으며 구조적 폐질환의 기왕력이 없는 21세 여성 환자였다[10]. 두 번째 보고된 증례는 특이 병력이 없는 59세 여성으로, 방사선 소견 상 다발성 공동이 있고 급속히 폐 경결이 진행하는 양상이었으며 좌측 주기관지 및 좌상엽 기관지를 침범한 형태였다[11]. 세 번째 증례는 이전 자궁경부암 수술 및 항암 치료 후 완치된 과거력이 있으나 폐질환의 기왕력이 없는 59세 여성으로, 흉부 전산화단층촬영 상 좌상엽 설상분절의 경화가 점차 진행하다 기관지 침범을 동반하게 된 사례였다[12]. 본 증례의 경우, 환자는 이전에 폐선암으로 인해 수술과 보조항암치료, 방사선 치료를 행한 적이 있으나 완치 판정 후 10년 이상 경과 후 발병한 사례로 구조적 폐질환이 있는 면역적격자의 기관지 침범 비결핵항산균 폐질환으로 보는 것이 적절하다. 국내의 기관지 침범형 NTM 폐질환은 본 증례를 포함한 4증례 모두 비흡연 여성이었으며 1예를 제외하고는 중년 이상의 여성에서 발병하였다. 또한, 본 증례는 M. intracelluare가 원인 균주였으나 나머지 3증례는 M. avium에 의한 감염이었다. 국내 증례들에서 면역적격자 기관지 침범형 NTM 폐질환의 원인 균주로 MAC이 주된 이유는 질환 자체의 희귀성과 더불어 M. avium complex가 국내 NTM 폐질환의 가장 많은 원인 균주를 차지함에 기인한 것으로 사료된다.
비결핵 항산균의 기관지 침범에 대한 발병기전은 아직 잘 알려져 있지 않으나 기관지 결핵과 유사할 것으로 추정된다[9]. 기관지 내시경 소견 역시 결핵과 구분되지 않아 부종성 점막, 육아종성 양상, 염증성 용종 및 궤양 등의 소견을 보인다. 본 증례는 타 국내 발병 증례들과 비교하여 기관지 내시경에서 보이는 건락성 괴사물질의 양이 매우 많았다는 것인데, 이는 이전의 폐암 수술로 인해 발생한 구조적 이상으로 인해 기관지 분비물의 배출이 어려웠던 것에 기인한 것으로 보인다. Meier 등[13]은 폐암 치료 이후 진단된 MAC 폐질환 13예 중 5명이 특별한 기저 질환이나 면역 저하 없이 발생하여 폐암 치료 이후 NTM PD가 알려진 위험 요인 없이도 호발하였음을 보고하였다. 본 증례는 폐암 치료에 의한 말단 기관지의 구조적 변형으로 NTM 균의 집락화 및 NTM PD 질환으로 진행하였을 것으로 추정하고 있다.
MAC 폐질환의 치료는 macrolide 감수성 MAC 균주의 경우, clarithromycin 또는 azithromycin에 rifampin, ethambutol의 3제를 병합하여 객담 배양 음전 후 최소 12개월 이상 유지하는 것을 권고하고 있다. 환자의 개별 상태 및 MAC 질환의 중증도에 따라 치료법을 달리하는데, 결절 기관지확장증형의 경우 주 3회 3제 투여하는 것을 권장하나 섬유공동형 및 심한 결절 기관지확장증형의 환자는 매일 치료요법이 권장된다[14]. 기관지를 침범한 MAC 질환에 대한 치료 권고사항은 확립된 바가 없으며, 본 증례의 환자는 중증 결절 기관지 확장형 MAC 감염에 준한다고 사료되어 clarithromycin, rifampin, ethambutol 3제 일일요법을 시행하였고, 치료 10개월 째 미생물학적, 임상적, 영상학적 호전을 보였다.
저자들은 10여 년 전 폐선암 치료 종료 후 재발없이 지내던 면역적격자에서 검사 상 기관지를 침범한 M. intracellulare 감염이 진단되었고, 약물 치료로 효과적인 반응을 보인 드문 증례를 경험하여 보고한다.
Notes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
FUNDING
None.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Hyeong Jun Cho wrote the manuscript and analyzed the data; Jongmin Lee, Chin Kook Rhee, Seung Joon Kim, Seok Chan Kim, Young Kyoon Kim collected the data and edited the manuscript. Ji Young Kang revised the manuscript.
Acknowledgements
None.