여러 내장에 재발한 다발고립형질세포종 1예
A Case of Multiple Solitary Plasmacytoma Recurring in Multiple Visceral Organs
Article information
Abstract
다발고립형질세포종은 고립형질세포종의 약 5%를 차지하는 매우 드문 질환이다. 저자들은 뼈의 다발고립형질세포종으로 치료받은 후 완전반응 상태를 유지하던 중, 여러 내장기관에 골수외형질세포종의 형태로 재발한 매우 드문 경우의 다발고립형질세포종을 경험하였다. 뼈의 다발고립형질세포종으로 치료받은 경력이 있는 68세 남자에서 배뇨곤란 및 변비가 발생하였다. 복부 및 골반의 전산화단층촬영에서 위, 췌장, 골반강 및 우측 둔부에 덩이가 발견되었으며, 위의 덩이에 대한 내시경 조직검사에서 형질세포종이 확인되었다. 이 환자는 내원 20개월 전, 우측 제 6 늑골 및 우측 장골의 다발고립형질세포종으로 방사선 치료를 받았고, 내원 14개월 전에는 좌측 제 5, 6, 7, 9 늑골에 재발하여 방사선 치료를 받았으며, 내원 12개월 전에는 제 5경추에 재발하여 방사선 치료 및 VAD 화학요법을 시행 받은 적이 있었다. 골반강의 덩이에 대한 방사선치료와 bortezomib + dexamethaone 화학요법으로 모든 덩이는 소실되었고, 8개월째 재발의 증거 없이 경과관찰 중이다. 향후 다발고립형질세포종의 임상 경과 및 치료와 예후인자에 관한 연구가 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
Trans Abstract
Multiple solitary plasmacytoma is a very rare disease entity, which occurs in up to 5% of patients with solitary plasmacytomas. We report an atypical case of multiple solitary plasmacytoma that recurred in multiple visceral organs without any evidence of bone marrow involvement. A 68-year-old male presented with voiding difficulty. Twenty months earlier, he had been placed on local radiotherapy for solitary plasmacytomas in the right 6th rib and right iliac bone. Recurrences were noted 14 and 12 months later in several ribs and the 5th cervical vertebra, respectively. These were well controlled with local radiotherapy and conventional systemic chemotherapy. He had multiple soft tissue masses in the stomach, pancreas, pelvic cavity, and right buttock. An endoscopic biopsy of the gastric mass confirmed the diagnosis of plasmacytoma. Local radiotherapy to the pelvic mass and systemic therapy consisting of bortezomib and dexamethasone were given, and he has been well for 8 months. (Korean J Med 2011;80:609-614)
서 론
다발고립형질세포종(multiple solitary plasmacytoma)은 고립형질세포종(solitary plasmacytoma)의 약 5%를 차지하는 매우 드문 질환으로, International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG)이 2003년에 제시한 기준에 따르면, 혈액과 소변에서 M-단백이 검출되지 않으면서, 클론성(clonal) 형질세포에 의한 골 파괴 또는 골수외 종양이 2개 이상 있고, 골수는 정상이며, 골격검색(skeletal survey)이 정상이고, 만약 시행되었다면 척추 및 골반의 자기공명영상이 정상이면서, 다발성골수종을 정의하는 이른바 ‘관련 기관 또는 조직의 손상’(related organ or tissue impairment, ROTI)이 없는 상태를 지칭하는 것으로, 때로 소량의 M-단백이 검출되기도 한다[1]. 그러나 다발고립형질세포종의 세부 분류기준은 아직 확실히 정립되지 않은 상태이며, 치료 및 예후 또한 알려진 바가 거의 없다. 저자들은 처음에는 뼈의 다발고립형질세포종(multiple solitary plasmacytoma of bone)으로 진단되어 치료를 받은 후 여러 내장에 골수외형질세포종의 형태로 재발한 매우 드문 형태의 다발고립형질세포종을 경험하였기에 문헌고찰과 함께 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
환 자: 68세, 남자
주 소: 배뇨곤란
현병력: 내원 20개월 전, 우측 장골과 우측 제6 늑골에 발생한 다발고립형질세포종이 확인되었다(Fig. 1). 당시 완전혈구계산, 일반화학검사 및 척추 자기공명검사를 포함한 골격검색에서는 특이사항이 없었고, 골수검사도 정상이었다. 혈청단백 전기영동 및 면역고정전기영동검사에서는 특이적 소견이 없었으나, 혈청 kappa와 lambda 유리경쇄(free light chain)가 각각 10.3 mg/L와 974.0 mg/L로 lambda 유리경쇄의 상승이 있었다(κ/λ = 0.01). 각각의 부위에 3,500 cGy의 방사선조사 후 혈청 lambda치는 정상화되었다. 내원 14개월 전에는 좌측 제5, 6, 7, 9 늑골에 재발하여 3,000 cGy의 방사선 치료를 받았다. 내원 12개월 전에는 제5경추에 재발하였다(Fig. 2). 당시에도 역시 골수검사는 정상이었고, 관련된 기관 또는 조직의 손상은 없으며, kappa와 lambda 유리경쇄는 각각 13.5 mg/L와 340.0 mg/L이었다(κ/λ = 0.04). 2,500 cGy의 방사선 치료 및 VAD (vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone) 화학요법이 5차례 시행되었으며, 다시 혈청 lambda 경쇄치는 정상화되었다. 이 기간 중 시행한 2회의 위내시경에서는 특이적 소견이 없었다. 이후 재발의 증거 없이 외래에서 추적관찰 중, 배뇨곤란 및 변비가 발생하였다.

(A) Computed tomography shows a 4.3 × 2.6 cm soft-tissue mass with destruction of the posterolateral arc of the right 6th rib (arrow). (B) Magnetic resonance imaging shows an enhancing 6.8 × 4.5 × 7.8 cm soft tissue mass in the right iliac bone adjacent to the sacroiliac junction (arrow). A biopsy of the mass in the right 6th rib revealed diffuse infiltration of plasma cells that are positive for CD 138 (C) and lambda light chain (D) on immunohistochemical staining (×400).
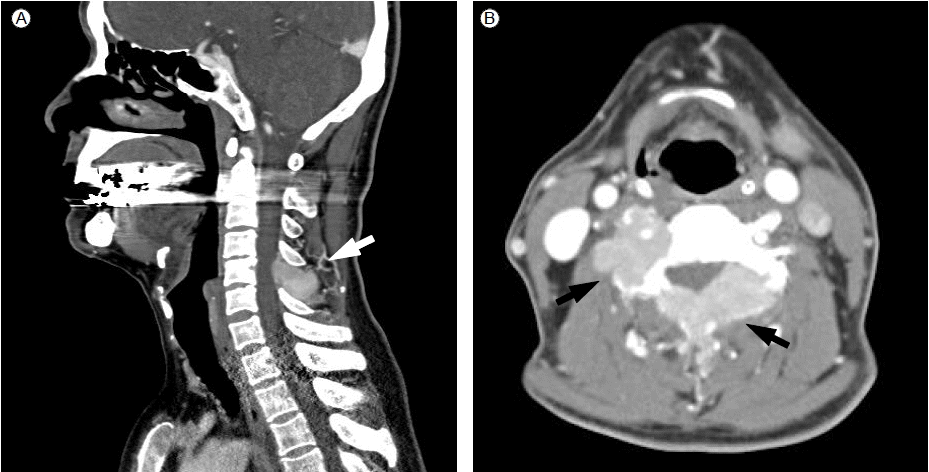
Magnetic resonance imaging shows plasmacytomas in the transverse process and both lamina of the 5th cervical vertebra (arrows).
신체 검진: 혈압은 120/80 mmHg, 맥박은 70회/분, 호흡수 20회/분, 체온은 37.0℃였다. 두경부, 흉부, 복부에 촉지되는 장기나 덩이는 없었으나, 우측 엉덩이에 2 × 2 cm 크기의 덩이가 만져졌고, 직장손가락검사에서 전립샘 부근에 단단하고 고정된 덩이가 만져졌다.
검사실 소견: 완전혈구계산에서 혈색소 10.3 g/dL, 적혈구용적 32.4%, 백혈구 4,690/μL, 혈소판 216,000/μL였다. 일반화학검사에서 혈청 총 단백 5.8 g/dL, 알부민 4.0 g/dL, 칼슘 9.0 mg/dL, 알칼라인포스파타제 48 IU/L, 혈액요소질소 17.4 mg/dL, 크레아티닌 0.9 mg/dL, 젖산탈수소효소(LDH) 285 IU/L였다. 혈청 IgG, IgA, IgM은 각각 564 mg/dL, 26 mg/dL, 30 mg/dL였고, β2-미세글로블린은 2.3 μg/mL였다. 혈청단백 및 뇨단백 전기영동검사에서는 특이사항이 없었다. 면역고정전기영동 검사에서는 lamda 경쇄 질환이 의심되었다. 혈청 kappa와 lambda 유리경쇄는 각각 6.81 mg/L와 677.0 mg/L였다(κ/λ = 0.01).
영상의학검사 및 상부위장관내시경 소견: 복부 및 골반의 전산화단층촬영에서 위, 췌장, 골반강 및 우측 엉덩이에 덩이가 발견되었다. 골반강의 덩이는 8.1 × 7.7 × 8.3 cm 크기로 전립샘과 곧창자 사이에 위치해 있었으며, 이질적으로 조영이 증강되었다(Fig. 3). 위내시경검사에서 체중부의 전벽측으로 직경 약 2.5 cm 가량의 두터운 유경성의 융기성 병변이 발견되었는데, 표면은 출혈괴와 백태가 붙어 있는 불규칙한 결정상이었다(Fig. 4).
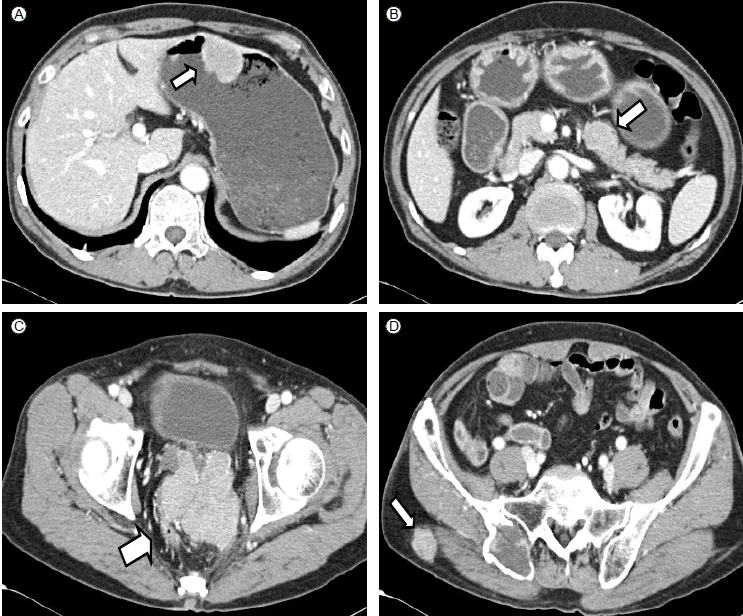
Computed tomography shows multiple soft tissue masses in the stomach (A), pancreas (B), pelvic cavity (C), and right buttock (D) (arrows).

(A) Gastroscopic examination revealed two polypoid masses with irregular surfaces covered by blood clots and whitish plaques in the body and anterior wall of the stomach. A biopsy of the mass showed the diffuse infiltration of plasma cells (B, H & E stain, ××400) that are positive for CD 138 (C) and lambda light chain (D) on immunohistochemical staining (×400).
병리소견: 위내시경을 이용한 위 덩이의 조직검사에서 CD138과 lambda 경쇄에 대한 면역조직화학 염색에 양성인 형질세포종으로 확인되었다(Fig. 4).
임상경과: 환자는 골반부위에 3,000 cGy의 방사선조사와 5차례의 bortezomib + dexamethasone 화학요법으로 치료 받은 후 모든 증상과 각 장기의 덩이는 소실되었고, 8개월째 재발의 증거 없이 추적관찰 중이다.
고 찰
IMWG가 제시한 기준에 따르면 단세포군감마글로불린병증은 monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), 무증상다발골수종, 증상다발골수종, 비분비골수종, 고립골형질세포종, 골수외형질세포종, 다발고립형질세포종, 형질세포백혈병 등으로 분류된다. 이 중 다발고립형질세포종은 고립형질세포종의 약 5%를 차지하는 매우 드문 질환이다[1]. 이번 증례는 처음에 뼈에 발생했던 다발고립형질세포종이 위, 췌장, 골반강 등에 골수외형질세포종의 형태로 재발하였는데, 골수외형질세포종이 위, 췌장, 골반강 등에 동시에 발생하는 경우는 거의 보고된 바 없다. 국소적 골수외형질세포종은 상부 호흡소화관에 비교적 흔한 편이고, 그 외에는 위장관의 다른 부위, 중추신경계, 방광, 갑상샘, 유방, 고환, 이하선 및 림프절에서 발생한 증례가 보고되었다[2]. Alexiou 등[3]의 보고에 따르면 골수외형질세포종이 위, 췌장, 및 직장에 각각 11.0%, 3.9%, 3.2% 발생하였다. 위에서 발생한 골수외형질세포종은 1928년 Vasiliu 등에 의해 처음으로 보고되었으며, 대개 골수외형질세포종의 2-5%을 차지하는 것으로 알려져 있다[4]. 위의 골수외형질세포종은 대개 무증상이거나 상복부 통증 및 팽만감, 오심 등의 증상을 일으키며, 위 내시경 및 외과적 치료 후, 조직검사를 통해 진단된다. 빈혈 또는 상부 위장관 출혈이 보고된 바 있고, H. pyroli와의 연관 가능성도 제시되었다[5]. 췌장에서 발생한 골수외형질세포종은 복통을 동반하거나, 정맥류 출혈을 일으킨다는 보고가 있다[6]. 이번 증례와 같이 고립골형질세포종이 골수외형질세포종으로 재발한 경우는 매우 드물며, Nolan 등[4] 및 Gaur 등[7]의 보고에 따르면 모두에서 위의 형질세포종으로 재발하였다. 전자의 증례에서는 수술적 치료 후, 결국 다발골수종으로 진행하였고, 후자의 경우는 수술 및 thalidomide + dexamethasone 화학요법 후 재발의 증거 없이 경과관찰 중이다.
고립골형질세포종 및 골수외형질세포종과는 달리 다발고립형질세포종은 매우 드물어 치료 및 예후에 대해 정리된 보고가 거의 없다. 고립골형질세포종의 경우, 일차적 치료는 방사선 치료로 80-90%의 반응률을 보이나, 대다수에서 다발골수종으로 진행하거나(56%), 다발골수종의 증거 없이 다른 골 부위에 고립 골 병변이 생기거나(2%), 국소 재발하는(11%) 세 가지 실패 양상을 보인다[8]. 고립골형질세포종은 과반수 이상에서 다발골수종으로 진행하고, 발생연령이 다발골수종보다 약 10년 정도 앞서며, 생존기간은 다발골수종보다 길으나 다발골수종으로 진행 후에는 생존기간이 거의 같으므로 다발골수종의 전 단계라는 주장도 있다. 고립골형질세포종의 예후인자로는 유리경쇄의 비율(κ/λ ratio)이 제시되었는데, 진단 시 유리경쇄의 비율이 비정상적일 경우 다발골수종으로 진행할 위험이 높았다[9]. 골수외형질세포종의 경우, 국소적 방사선 치료에 95% 이상의 반응률을 보이지만, 15%에서 다발성골수종으로 진행하고, 10%에서 다른 부위에 재발하며, 7.5%에서 국소 재발한다는 보고가 있다[2].
위에 발생한 형질세포종의 치료로는 위 및 주위 림프절에 국한되어 발견된 경우는 외과적 절제술이나 국소적 방사선 치료를 하여 좋은 성과를 거둘 수 있으며, 외과적 절제술 후 방사선 병용 치료를 시행한 경우도 있었다[4]. 그러나 치료와 병기에 따른 예후에 관해서는 아직 보고된 바가 없다. 췌장에서 발생한 형질세포종은 외과적 절제술 및 방사선 치료, 그리고 bortezomib에 의한 화학요법으로 좋은 성과가 있다는 보고가 있다[10]. 이 환자의 경우는 덩이의 크기가 큰 골반강에 대한 국소 방사선조사와 함께 bortezomib + dexamethasone 화학요법을 병행하여 완전반응이 유도되었다. 처음 진단받았을 때와 재발하였을 때마다 혈청 lambda 유리경쇄의 상승이 있었고, 치료 후 정상화되었던 점으로 보아 질병의 진행 여부의 판단에 혈청 유리경쇄 검사가 도움이 될 것으로 생각된다.
다발고립형질세포종이라는 용어는 2003년 발표된 IMWG에 의해 처음 소개되었으나, 아직 그 분류기준에는 논란의 여지가 있다[1]. 아울러 이번 증례에서와 같이 뼈의 다발고립형질세포종이 다발골수종이 아닌 다발고립골수외형질세포종의 형태로 재발한 경우는 처음 보고되는 것으로 판단되는 바, 향후 다발고립형질세포종의 임상 경과 및 효과적인 치료와 예후인자에 대한 추가적인 연구가 필요할 것으로 생각된다.